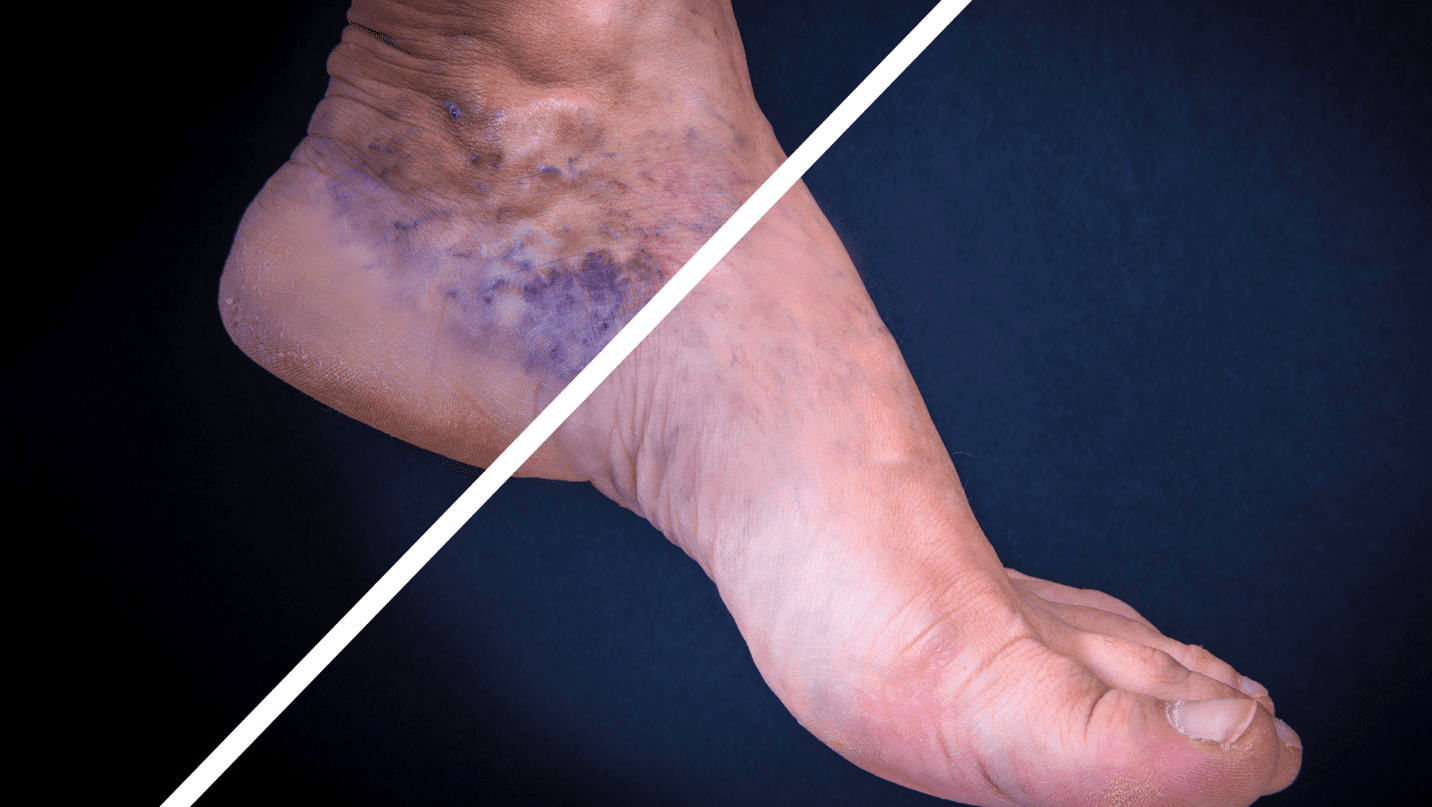
Venous insufficiency, often referred to as chronic venous insufficiency (CVI), is a vascular condition where the leg veins struggle to return blood to the heart. This disorder can lead to the visible manifestation of varicose veins, which are swollen, twisted veins appearing mostly on the legs and feet.
Venous insufficiency occurs when the one-way valves in the veins, which prevent blood from flowing backward, become damaged or weak. As a result, blood accumulates in the veins, leading to increased pressure and dilated vessels. Over time, this may result in varicose veins and other symptoms.
Symptoms of Venous Insufficiency
Beyond the appearance of varicose veins, venous insufficiency can cause several symptoms including:
- Leg pain or cramps
- Itching or tingling
- Swelling in the lower legs and ankles, especially after prolonged standing or sitting
- Skin discoloration or texture changes
- Leg ulcers
It’s essential to recognize these signs early. If left untreated, CVI can result in more severe complications, such as skin ulcers or blood clots.
Causes and Risk Factors
Factors contributing to venous insufficiency include:
- Age: The risk increases with age due to wear and tear on vein valves.
- Gender: Women are more prone, possibly due to hormonal changes that relax vein walls.
- Family history: If other family members had varicose veins, you’re more likely to develop them.
- Obesity: Added weight can increase the pressure on your veins.
- Standing or sitting for long periods: This can force your veins to work harder to counteract gravity and send blood back to the heart.
Treatment Options
Today, there are several innovative treatments for venous insufficiency and varicose veins, including:
- Compression therapy: Wearing compression stockings helps reduce leg swelling and relieves other symptoms.
- Endovenous laser and radiofrequency treatment: A minimally invasive procedure using laser energy to seal affected veins.
- Venaseal and Sclerotherapy or Varithena: This involves injecting a solution into the vein, causing it to scar, which redirects blood to healthier veins.
- Surgery: In more severe cases, surgical interventions, like vein stripping or ligation, may be recommended.
Consulting a vascular specialist is vital to determine the best treatment plan tailored to individual needs.
Prevention and Management
While certain risk factors like age or genetics can’t be controlled, lifestyle changes can reduce the risk of developing venous insufficiency and manage its symptoms:
- Exercise regularly to improve leg strength and circulation.
- Elevate your legs when resting.
- Watch your weight and diet.
- Avoid long periods of standing or sitting.
Conclusion
Venous insufficiency and varicose veins are more than cosmetic concerns; they can significantly impact quality of life and may lead to further complications if not addressed. By understanding the condition, recognizing its signs, and adopting preventive measures, one can ensure better vascular health. Contact New York Medical and Vascular Care if you suspect you have venous issues.
Highlighted Keywords:
- Venous insufficiency
- Varicose veins
- Vascular condition
- Leg pain
- Leg swelling
- Leg cramping
- Chronic venous insufficiency (CVI)
- Compression therapy
- Endovenous laser treatment (EVLT)
- Radiofrequency ablation
- Venaseal
- Varithena
- Sclerotherapy
- Vascular specialist
Written by Dapralab